Understanding the difference between “response” and “respond” can enhance your communication skills and improve clarity in both written and spoken interactions.
While these terms might seem similar, they serve different purposes in language.
Master the difference between “response” (a noun for reactions or answers) and “respond” (a verb for the act of replying) to communicate more clearly and effectively.
This guide will explore the distinctions, usage rules, and practical applications of each term to help you use them effectively.
Key Differences Between “Response” and “Respond”
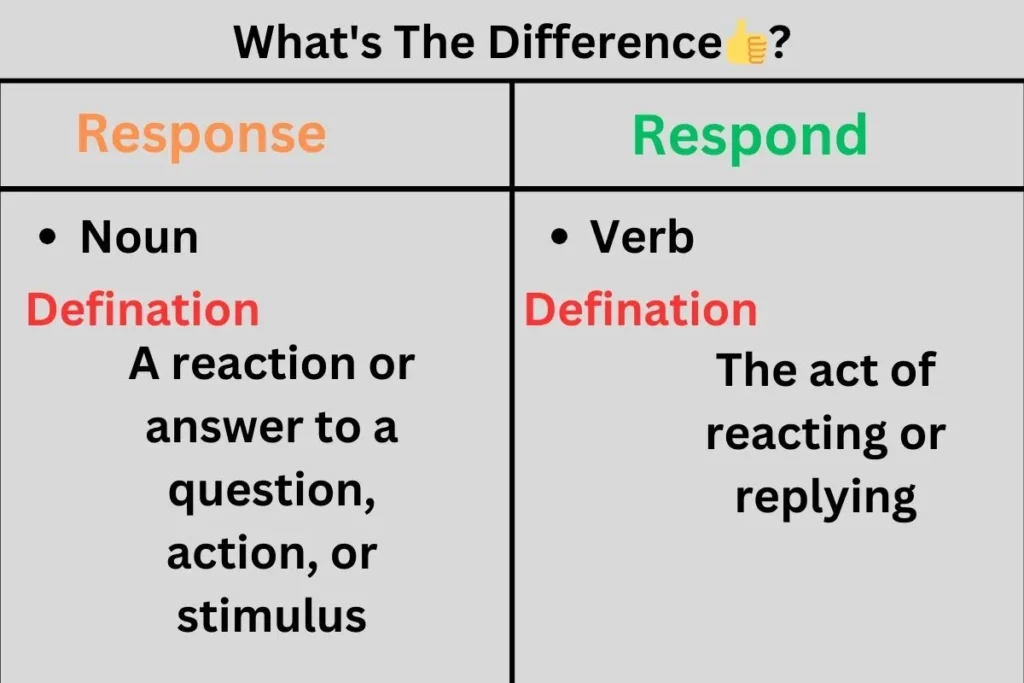
| Term | Part of Speech | Definition | Usage | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Response | Noun | A reaction or answer to a question, action, or stimulus | Refers to the outcome or result | “Her response to the feedback was positive.” |
| Respond | Verb | The act of reacting or replying | Describes the action of giving an answer or reaction | “He didn’t respond to the email right away.” |
Unraveling Definitions
Definition of “Response”
“Response” is a noun that refers to a reaction or answer to a stimulus, question, or event.
It signifies the outcome or result of an action or situation. For instance:
- Customer Service: A company’s reply to a customer’s complaint is a response.
- Scientific Research: The change observed in an experiment as a result of a variable is a response.
Definition of “Respond”
“Respond” is a verb that describes the act of reacting or replying.
It involves the process of providing an answer or reaction to a stimulus or query. For example:
- Personal Interaction: When someone asks you a question, your reply is to respond.
- Emergency Situation: A medical professional’s actions in an urgent scenario are to respond to the situation.
Grammar Essentials
Usage Rules for “Response”
- When to Use: Employ “response” when referring to the outcome or reaction itself.
It is used to describe the result of an action or the content of a reply. - Examples:
- “The response to the new policy was overwhelmingly positive.”
- “Her response to the email was prompt and thorough.”
Usage Rules for “Respond”
- When to Use: Use “respond” when discussing the action of replying or reacting. It emphasizes the process or act of answering.
- Examples:
- “He didn’t respond to the invitation right away.”
- “The team must respond quickly to customer feedback.”
Response in Action: Real-World Noun Usage
In various fields, “response” is used to denote the result or reaction to an event or action.
Here are some practical examples:
- Customer Service:
- Response Time: The speed at which a company addresses customer inquiries or complaints.
- Feedback: “The response from customers was used to improve the service.”
- Scientific Research:
- Data Collection: “The response variable in the experiment showed significant changes.”
- Observation: “Researchers analyzed the response to different stimuli.”
Clarifying Misconceptions
Often, people confuse “response” with “respond” due to their similarities.
Here are common errors and how to avoid them:
- Error: Using “response” as a verb.
- Incorrect: “I will response to your email.”
- Correct: “I will respond to your email.”
- Error: Using “respond” as a noun.
- Incorrect: “The respond was immediate.”
- Correct: “The response was immediate.”
How ‘Response’ Captures the Result
“Response” is particularly useful in contexts where the outcome or result is important.
Here’s how it works in different scenarios:
- Handling Complaints:
- Response to Complaints: “The company’s response to customer complaints is crucial for maintaining satisfaction.”
- Example: “After receiving several complaints, the company’s response included policy changes and additional training for staff.”
- Receiving Compliments:
- Acknowledgment: “A thoughtful response to compliments can strengthen relationships and boost morale.”
- Example: “Her response to the praise was humble and appreciative.”
Medical and Emergency Contexts: The Importance of Prompt ‘Response’
In medical and emergency settings, the term “response” is critical.
It signifies the importance of timely actions in saving lives and managing crises.
- Medical Response:
- Emergency Care: “A swift response by medical personnel can significantly impact patient outcomes.”
- Example: “In cases of cardiac arrest, immediate response with CPR can be life-saving.”
- Emergency Services:
- Timeliness: “Emergency services’ response times are often measured to ensure efficiency.”
- Example: “City officials track response times to improve emergency response strategies.”
Respond’s Verb Form: Identifying Interactive Scenarios
“Respond” as a verb highlights the act of reacting or replying in various interactive scenarios.
It emphasizes the action rather than the result.
- Interactive Scenarios:
- Conversations: “When asked a question, one must respond clearly and promptly.”
- Professional Settings: “Employees should respond to emails and messages in a timely manner.”
- Examples from Daily Life:
- Personal Interaction: “She didn’t respond to his text message until the next day.”
- Customer Service: “The support team must respond to customer queries within 24 hours.”
Examples from Literature and News
Analyzing how “response” and “respond” are used in literature and news can provide deeper insights.
- Literary Examples:
- Novel Analysis: “In classic literature, characters often have a notable response to pivotal events.”
- Example: “In Pride and Prejudice, Elizabeth Bennet’s response to Mr. Darcy’s proposal is central to the plot.”
- News Media:
- Recent Reports: “News reports frequently highlight the response of public figures to major events.”
- Example: “The response of government officials to natural disasters is often covered in depth.”
Psychological Perspective: Behavioral Responses vs. Physical Responding
Understanding “response” from a psychological viewpoint can offer insights into human behavior.
- Behavioral Responses:
- Psychological Theories: “Behavioral responses are influenced by cognitive and emotional factors.”
- Example: “In psychology, how individuals respond to stress is studied to understand coping mechanisms.”
- Physical Responses:
- Physiological Aspects: “Physical responses include physiological changes like increased heart rate or sweating.”
- Example: “The body’s response to danger involves the fight-or-flight mechanism.”
Emotional Contagion: How Individuals ‘Respond’ to Others’ Feelings
Emotional contagion explores how people’s emotions influence each other, reflecting the verb “respond.”
- Emotional Impact:
- Social Interactions: “People often respond to the emotions of others, such as feeling happy when someone else is joyful.”
- Example: “In group settings, one person’s anxiety can lead to a collective response of stress.”
- Case Studies:
- Study on Empathy: “Research shows that empathetic individuals are more likely to respond positively to others’ feelings.”
- Example: “Studies on emotional contagion reveal how individuals respond to group dynamics.”
Decision Making: The Cognitive ‘Response’ to External Stimuli
The cognitive aspect of “response” involves how we process and react to external stimuli.
- Cognitive Processes:
- Decision Making: “Our cognitive response to external stimuli influences our decisions and actions.”
- Example: “When faced with a choice, our brain’s response can determine our final decision.”
- Role in Decision Making:
- Stimulus and Reaction: “The speed and type of response can affect decision outcomes.”
- Example: “Rapid responses in high-pressure situations often lead to instinctive decisions.”
Etymology and Evolution
Tracing the origins and evolution of “response” and “respond” can deepen our understanding of their usage.
- Origins of “Response”:
- Etymology: “Derived from the Latin word ‘respondere,’ meaning ‘to answer.‘”
- Historical Use: “Initially used to denote replies in formal contexts.”
- Origins of “Respond”:
- Etymology: “Also comes from Latin ‘respondere,’ but used as a verb.”
- Evolution: “The verb form evolved to represent the action of replying.”
Improving Communication Skills
Mastering the use of “response” and “respond” can enhance your communication effectiveness.
Here are some tips:
- Tips for Correct Usage:
- Understand the Context: “Determine whether you need a noun or verb based on the situation.”
- Practice: “Use both terms in varied sentences to solidify your understanding.”
- Common Pitfalls:
- Avoid Confusion: “Ensure you’re using ‘response‘ as a noun and ‘respond‘ as a verb.”
- Double-Check: “Review your writing to catch any misuse of these terms.”
Conclusion
Understanding the distinctions between “response” and “respond” is crucial for clear and effective communication.
By recognizing their grammatical roles and applying them appropriately, you can improve your writing and speaking skills.
Remember to practice using these terms correctly and consider their usage in different contexts to enhance your overall communication.
This blog post provides an in-depth exploration of “response” vs. “respond,” offering clear definitions, usage rules, and practical examples to help you master these terms.

As an experienced English teacher, I’m Jessica Thompson, here to make grammar and vocabulary simple and fun. Join me on TalkSpeaker as we explore the language together, one lesson at a time!