Understanding the difference between “affect” and “effect” is a challenge that many people face, even those with years of writing experience.
While both words are commonly used in the English language, they have distinct meanings and uses.
Affect is a verb that means to influence, while effect is a noun referring to the result of that influence.
This post will help you grasp the clear distinction between the two and improve your writing by using them correctly in different contexts.
Whether you’re a student, writer, or someone who simply wants to fine-tune their communication, this guide will provide you with in-depth knowledge, practical tips, and real-world examples.
Let’s Jump into the specifics of “affect” and “effect” to clear up any confusion.
Key Differences Between Affect and Effect
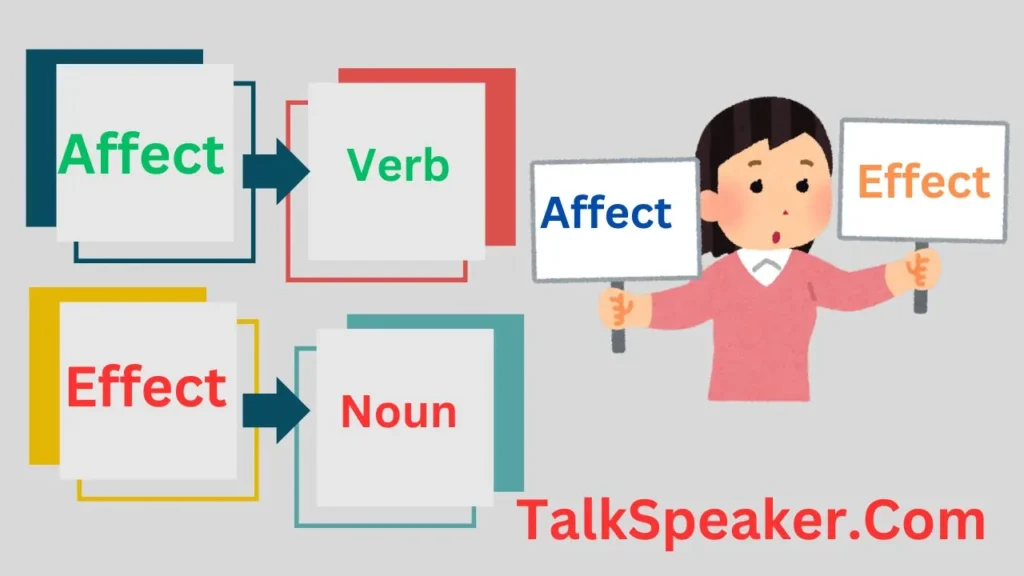
Let’s make the distinction crystal clear:
| Word | Part of Speech | Meaning | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Affect | Verb | To influence or change something. | “The news affected his decision.” |
| Effect | Noun | The result or outcome of an action. | “The effect of the news was apparent.” |
What is “Affect”?
Affect is primarily used as a verb, and it refers to the action of influencing or producing a change in something.
It’s about how something has an impact or influence on another thing.
Examples of “Affect” in Sentences:
- The weather can affect your mood—In this example, the weather is influencing the mood.
- Her speech affected everyone deeply—The speech had an impact on the emotions of those present.
In these examples, “affect” is a verb, acting as the action of changing something else.
Quick Tip:
If you are referring to an action or influence, “affect” is the right word to use.
It is a verb that shows something causing a change or influence.
What is “Effect”?
On the other hand, “effect” is mainly used as a noun. It refers to the result or consequence of a change.
Essentially, “effect” is the outcome or what happens as a result of an influence or action.
Examples of “Effect” in Sentences:
- The new law had a positive effect on the community—In this sentence, the new law’s result is the positive change in the community.
- The effect of the medication was immediate—The result or outcome of taking the medication is described here.
Quick Tip:
If you’re talking about a result or outcome, use “effect”, the noun form.
It points to the result of an action.
Summary of Differences:
- Affect = Verb (Action): It’s the influence or change.
- Effect = Noun (Result): It’s the outcome or result.
Mnemonic to Remember:
- Affect = Action (Both start with A).
- Effect = End result (Both start with E).
When “Affect” and “Effect” Are Used in Psychology
The terms “affect” and “effect” also have specific uses in psychology.
Affect in Psychology:
In psychology, “affect” refers to an emotional response or feeling. This term describes a person’s outward emotional expression.
For example, a person may have a flat affect, which means their emotional expressions are minimal or unresponsive.
- Example: “The patient’s affect was flat during the interview.” In this case, “affect” refers to the patient’s emotional response or lack thereof.
Effect in Psychology:
In psychology, “effect” is often used to refer to the result or outcome of a psychological intervention or condition.
It can describe how a therapy, drug, or situation impacts a person’s behavior or mental state.
- Example:
“The effect of the new drug on depression was observed in the study.” Here, “effect” describes the result or outcome of the drug.
Exceptions and Special Cases
While “affect” and “effect” are generally used as a verb and noun, respectively, there are exceptions worth mentioning.
Affect as a Noun:
Though less common, “affect” can also be used as a noun in certain contexts, particularly in psychology.
As a noun, “affect” describes a person’s emotional state or expression.
- Example:
“The patient’s affect was inappropriate for the situation.” In this case, “affect” is used as a noun to refer to the emotional display.
Effect as a Verb:
While it’s rare, “effect” can be used as a verb meaning to bring about or cause something to happen.
This usage is typically formal and seen more in academic or legal writing.
- Example: “The new law will effect change in the education system.” Here, “effect” means to bring about or cause a change.
Common Mistakes and Misuses
The confusion between affect and effect often leads to common mistakes.
Here are some examples of incorrect usage and how to fix them:
Incorrect:
- “The weather had an affect on his health.”
- Correct: “The weather had an effect on his health.”
Incorrect:
- “The movie really effected me.”
- Correct: “The movie really affected me.”
Explanation of Mistakes:
- The word affect is a verb, so it should be used when you want to describe an action or influence. In the first example, the weather is influencing health, so “effect” is the correct choice.
- The word effect is a noun, meaning the result or outcome. In the second example, “effected” should be changed to “affected”, since the sentence describes the emotional impact (an action).
Practical Tips for Using Affect and Effect Correctly
To avoid confusion, here are a few tips:
General Rule:
- If you’re describing an action or influence, use affect (the verb).
- If you’re referring to the result or consequence of something, use effect (the noun).
Quick Check:
- Affect is often used with emotions, behaviors, and changes.
- Effect is used to describe the result of something.
Other Tricks:
- When writing about an outcome, use effect.
- When describing how something influences something else, use affect.
How to Remember the Difference
Here are a few tips to help you remember which word to use:
- Affect = Action: If you can swap the word with another verb like “change,” it’s likely affect.
- Effect = End result: If you can swap the word with another noun like “outcome,” it’s likely effect.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can “Affect” Ever Be a Noun?
Yes, though rare, “affect” is used as a noun in psychology. It refers to a person’s emotional response or state.
Can “Effect” Be a Verb?
Yes, though less common, “effect” can be used as a verb meaning to cause something to happen.
What’s the Best Way to Avoid Confusion Between Affect and Effect?
Keep the following in mind:
- Affect = Action (verb).
- Effect = End result (noun).
Can the Confusion Be Prevented?
Absolutely! By practicing these rules and using the words in context, the difference will become second nature.
What is the difference between affect and effect?
Affect is a verb that means to influence something, while effect is a noun referring to the result or outcome of a change.
Can “affect” ever be used as a noun?
Yes, though rare, “affect” can be used as a noun in psychology to describe a person’s emotional response, like “flat affect.”
Can “effect” be used as a verb?
Yes, although less common, “effect” can be used as a verb meaning to bring about or cause something to happen.
How do I remember when to use affect or effect?
Use “affect” when referring to an action or influence (verb), and use “effect” when talking about the result or outcome (noun).
Why do people confuse affect and effect?
The confusion often arises because both words are similar in meaning, but one refers to an action (affect) and the other to the result of that action (effect).
Conclusion:
The distinction between affect and effect doesn’t have to be confusing once you understand their core meanings. By remembering that “affect” is an action (verb) and “effect” is a result (noun), you’ll avoid making mistakes in your writing.
Whether you’re writing essays, emails, or creating content for blogs, using these words correctly will help you communicate clearly and effectively.
By mastering these terms, you’ll sound more polished in your writing and avoid the common grammatical missteps that can detract from your credibility.
Keep practicing, and soon the difference between affect and effect will become second nature!

As an experienced English teacher, I’m Jessica Thompson, here to make grammar and vocabulary simple and fun. Join me on TalkSpeaker as we explore the language together, one lesson at a time!